Have you ever wondered how the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) collects and analyzes financial data from public companies? The Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval (EDGAR) system is a powerful tool that enables the SEC to fulfill its mission of protecting investors and maintaining fair, orderly, and efficient markets.
The Challenges of Data Collection
Before the implementation of EDGAR, companies filed their financial reports with the SEC on paper. This process was time-consuming and inefficient, making it difficult for the SEC to quickly and accurately review and analyze the data. Additionally, the public had limited access to this information, hindering their ability to make informed investment decisions.
The Solution: EDGAR
EDGAR was introduced in 1993 as a centralized electronic system for collecting, analyzing, and retrieving financial data from public companies. EDGAR revolutionized the SEC’s operations by enabling companies to file their reports electronically, ensuring their timely and accurate submission. It also made financial data more readily available to the public, increasing transparency in the markets.

SOLUTION: Electronic data gathering analysis and retrieval system edgar – Source www.studypool.com
What is EDGAR?
EDGAR is a comprehensive system that encompasses a wide range of functionalities for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating financial data. It allows companies to submit their SEC filings electronically, including annual reports (10-K), quarterly reports (10-Q), and other periodic reports. EDGAR also provides a robust search engine that enables users to retrieve specific filings by company name, ticker symbol, or filing type.
History and Evolution of EDGAR
EDGAR was initially developed in the early 1990s as a response to the inefficiencies of the paper-based filing system. Over the years, EDGAR has undergone several upgrades and enhancements to keep pace with technological advancements and the evolving needs of the SEC and the public. In 2007, EDGAR underwent a major upgrade known as “EDGAR 2.0,” which introduced a new user interface and enhanced search capabilities.
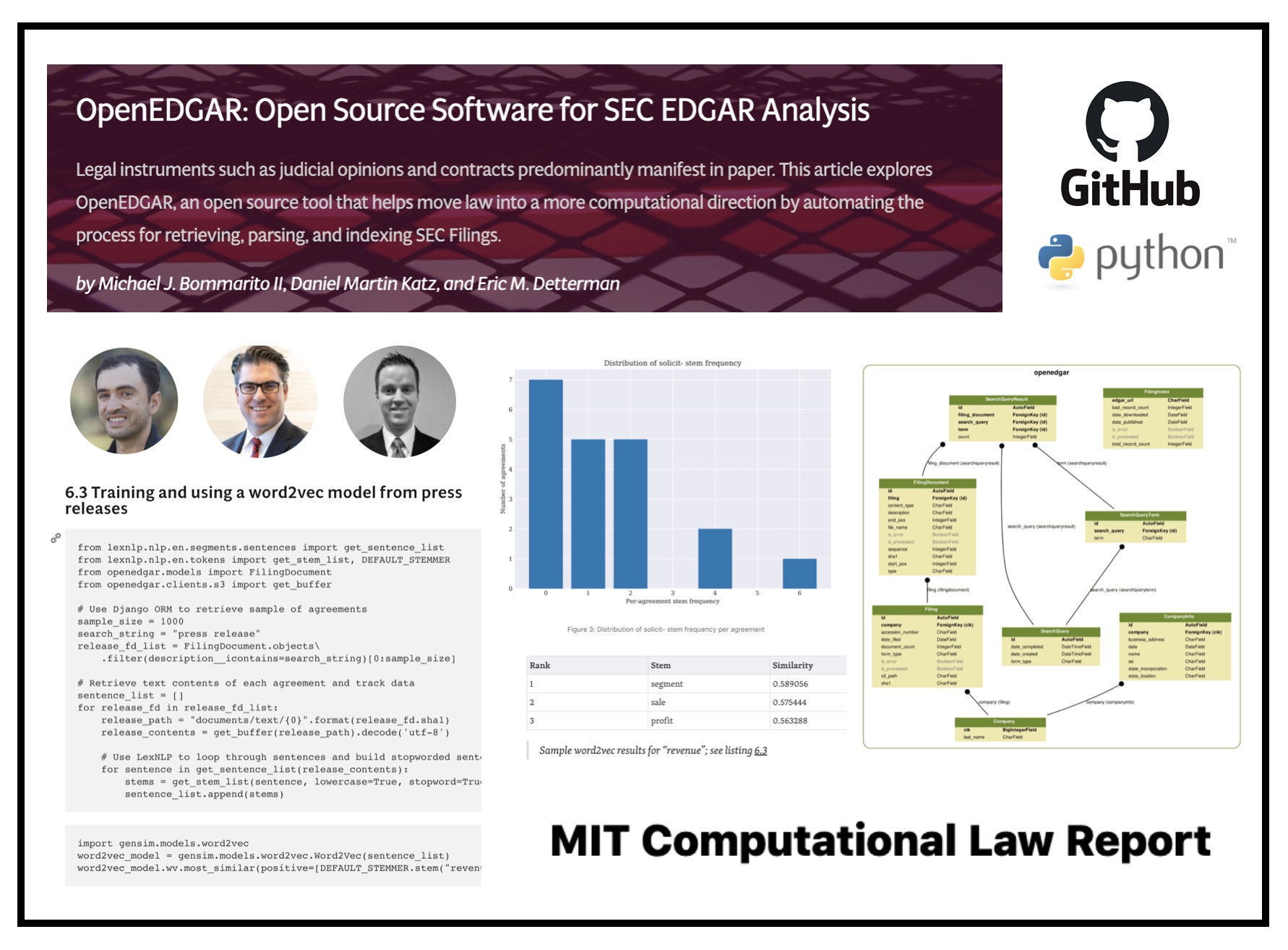
OpenEDGAR: Open Source Software for SEC EDGAR Analysis is published in – Source computationallegalstudies.com
The Hidden Secret of EDGAR
Beyond its core functionalities, EDGAR offers a hidden gem known as “XBRL” (Extensible Business Reporting Language). XBRL is a standardized electronic format for representing financial data. By submitting their filings in XBRL format, companies enable the SEC and other users to analyze and compare their financial data more efficiently and effectively. XBRL enhances the transparency and accuracy of financial reporting, making it easier for investors and analysts to make informed decisions.
EDGAR Recommendations
To maximize the benefits of EDGAR, consider the following recommendations:
- Use the advanced search features to quickly find specific filings.
- Subscribe to email alerts for filings from companies you follow.
- Download and analyze financial data in XBRL format for deeper insights.
Importance of EDGAR for Investors and Analysts
EDGAR is an invaluable resource for investors and analysts. It provides timely access to financial data, allowing them to make informed investment decisions. By analyzing EDGAR filings, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health, growth prospects, and risk factors. Analysts use EDGAR to assess companies’ competitive position, industry trends, and potential investment opportunities.

SEC Filings Overview – IPOHub – Source www.ipohub.org
Tips for Using EDGAR
To effectively navigate and utilize EDGAR, follow these tips:
- Understand the different types of EDGAR filings.
- Use keywords and search filters to narrow down your search.
- Access EDGAR through the SEC website or authorized third-party providers.
EDGAR as a Tool for Research and Analysis
EDGAR is not just a database of financial filings; it’s a powerful research and analysis tool. By extracting and analyzing data from EDGAR filings, analysts can uncover trends, identify anomalies, and make predictions about the markets. EDGAR’s vast repository of data enables researchers to conduct in-depth studies on corporate finance, industry dynamics, and economic indicators.

A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding and Analyzing Financial Disclosures – Source info.radientanalytics.com
Fun Facts About EDGAR
Did you know?
- EDGAR processes over 6 million filings annually.
- The EDGAR database contains over 110 million filings.
- EDGAR’s website receives over 250 million page views per year.
How to Access EDGAR
Accessing EDGAR is simple and straightforward. To access EDGAR, visit the SEC website at www.sec.gov/edgar. You can also subscribe to email alerts for filings from specific companies or industries.
What if EDGAR Didn’t Exist?
Imagine if EDGAR didn’t exist. Financial data would be scattered across paper files, making it difficult to access and analyze. Public companies would face significant challenges in filing their reports on time, and investors would have limited access to information. Without EDGAR, the markets would be less transparent and efficient.

Collecte, analyse et récupération de données électroniques (EDGAR – Source thepressfree.com
Listicle of EDGAR Benefits
Here’s a listicle summarizing the key benefits of EDGAR:
- Electronic filing for timely and accurate submissions.
- Public access to financial data for increased transparency.
- XBRL format for enhanced data analysis and comparison.
- Advanced search capabilities for easy retrieval of specific filings.
- Email alerts for filings from specific companies or industries.
Question and Answer Section
Q: What is the purpose of EDGAR?
A: EDGAR is a system for collecting, analyzing, and retrieving financial data from public companies.
Q: How do I access EDGAR?
A: You can access EDGAR through the SEC website at www.sec.gov/edgar.
Q: What is XBRL?
A: XBRL is a standardized electronic format for representing financial data.
Q: How can I use EDGAR for research and analysis?
A: By extracting and analyzing data from EDGAR filings, you can uncover trends, identify anomalies, and make predictions about the markets.
Conclusion of EDGAR: The Electronic Data Gathering, Analysis, and Retrieval System For SEC Filings
EDGAR is a cornerstone of the SEC’s operations, enabling efficient and transparent financial reporting. It has revolutionized the way that companies file their reports and the way that investors and analysts access financial data. EDGAR’s continued evolution and enhancements will ensure its relevance and effectiveness in the years to come.
